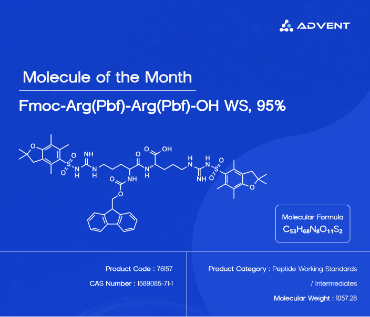
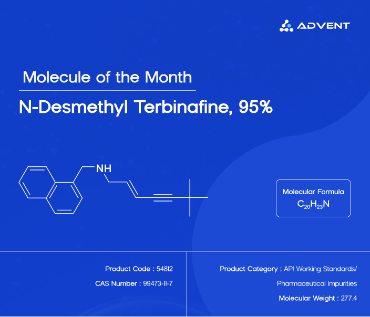
In Mohanty Masterclass Episode 11, Dr. Mohanty takes us through an in-depth exploration of Nitrosamines, a class of chemical compounds that have become an increasingly important subject in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Despite their small structure, nitrosamines pose significant health risks, primarily due to their carcinogenic and mutagenic properties. This article dives deep into what nitrosamines are, how they form, the history of their detection, and their profound impact on drug safety regulations.
What Are Nitrosamines?
Nitrosamines are chemical compounds that feature a nitroso group (-NO) attached to an amine group (-NH). This unique structure plays a crucial role in their biological activity. Many nitrosamines are classified as probable human carcinogens, which means they can potentially cause cancer. Furthermore, they are mutagenic—meaning they can alter DNA, leading to increased cancer risks even at very low concentrations.
The most well-known nitrosamines include N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) and N-Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA), which have been identified in various pharmaceutical products and strongly linked to cancer. For instance, N-Nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutyric acid (NMBA), another well-known nitrosamine, has caused product recalls in antihypertensive drugs. The discovery of these dangerous impurities has raised significant concerns within the pharmaceutical industry, urging an overhaul of manufacturing practices and stricter testing protocols.
How Do Nitrosamines Form?
Nitrosamines typically do not form intentionally. Instead, they arise as by-products or impurities during chemical reactions, processing, or storage. The formation of nitrosamines occurs when nitrosating agents, such as nitrites, react with secondary or tertiary amines under specific conditions, such as high temperatures or acidic environments. This reaction is more likely during certain stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
For instance, nitrites like sodium nitrite may be present in solvents or as impurities in raw materials. These nitrites, when they react with amines used in drug synthesis, can create nitrosamines. Cross-contamination from poorly cleaned manufacturing equipment or residual nitrites in solvents can further heighten the risk. Even raw materials or excipients from unqualified suppliers may introduce nitrite impurities, contributing to the formation of nitrosamines.
The Evolution of Nitrosamine Awareness in Pharmaceuticals
The nitrosamine issue came to the forefront in 2018 when N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) was detected in valsartan, a widely used antihypertensive drug. This revelation triggered immediate recalls in several countries, including the United States and Europe. By 2019, other nitrosamines, such as NDEA and NMBA, were discovered in additional batches of valsartan, as well as in other sartan drugs like Losartan and Irbesartan. This showed that nitrosamine contamination was not isolated but rather a systemic issue linked to raw materials, solvents, and manufacturing processes.
In 2020, the discovery of nitrosamines in ranitidine, a common anti-ulcer drug, led to further global recalls. This raised concerns that even finished pharmaceutical formulations could generate nitrosamines during storage. As a result, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued urgent guidance, urging manufacturers to review their processes and assess the risk of nitrosamine formation in their products. Regulatory agencies also established acceptable intake limits, testing requirements, and risk assessment strategies for nitrosamines in drug products.
The nitrosamine issue has evolved from an unexpected impurity to a global regulatory priority, reshaping how the pharmaceutical industry views drug safety and prompting widespread changes in the way drugs are manufactured and tested.
The Concerns Around Nitrosamines
The presence of nitrosamines in pharmaceuticals has raised several concerns, most notably in relation to patient health risks. Nitrosamine contamination has led to drug recalls, impacting millions of patients worldwide. For example, the withdrawal of antihypertensive drugs like valsartan has caused significant disruption in the healthcare system, as these medications are critical for managing conditions like high blood pressure.
Additionally, economic consequences have been substantial. Drug recalls are costly for pharmaceutical companies, not only due to the direct cost of recalling products but also because of regulatory fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. Reformulating affected products and navigating the regulatory landscape also lead to delayed product launches, higher development costs, and additional clinical complexities.
Detection and Analysis of Nitrosamines
Detecting nitrosamines in pharmaceutical products is a significant challenge due to their presence at ultra-trace levels. Specialized analytical techniques are required to identify and quantify these impurities. Some commonly used methods include:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Effective for identifying volatile nitrosamines.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Ideal for non-volatile nitrosamines, offering high sensitivity.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Useful when combined with other detectors for nitrosamine analysis.
Ion Chromatography: Effective for detecting nitrite and nitrate ions, precursors to nitrosamine formation.
These sophisticated techniques require high-quality solvents and reagents, as even minute contamination can compromise results. This highlights the importance of strict quality controls and contamination prevention in the detection process.
ADVENT's Role in Nitrosamine Detection
ADVENT, a leader in providing chemical standards, plays a critical role in helping pharmaceutical companies detect nitrosamines in their products. The company has developed high-purity nitrosamine working standards for quantitative analysis, assisting manufacturers in ensuring their products meet stringent regulatory guidelines.
ADVENT’s working standards are available in customizable packs, along with certificates of analysis (CoA) that include detailed characterization data. These standards are essential for reliable nitrosamine testing, enabling pharmaceutical companies to measure these impurities accurately and adhere to global safety regulations.
Conclusion: Moving Towards Safer Pharmaceutical Practices
In conclusion, nitrosamines are unintended but highly dangerous impurities that demand the pharmaceutical industry's full attention. They not only pose health risks but have also led to numerous drug recalls, disrupting supply chains and incurring significant economic losses. However, these challenges have spurred innovation in chemical manufacturing and testing methods, reshaping industry standards and emphasizing the importance of safer processes.
As global regulatory bodies continue to refine their guidelines and testing protocols, the industry is adopting more robust quality controls and risk management strategies. With the growing awareness of nitrosamine risks, pharmaceutical manufacturers are now focusing on cleaner processes, improved raw material control, and more sophisticated detection methods to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products.
Mohanty Masterclass Episode 11 provides a comprehensive introduction to nitrosamines and their impact on the pharmaceutical industry. By exploring the history, formation, and detection of these compounds, Dr. Mohanty offers invaluable insights into how the industry is responding to this emerging threat. Stay tuned for future episodes of the Masterclass, where Dr. Mohanty will continue to explore other important topics in the world of pharmaceutical safety and innovation.